What is a Convolutional Neural Network?
A Convolutional Neural Network(CNN) is an Artificial Neural Network in which at least one of the layers performs a convolution on the input.
What’s a Convolution?
A convolution is a mathematical operation where we take the input matrix, and pass a smaller matrix known as the kernel or filter over top of it. When we do so, we perform matrix multiplication between the kernel and the portion of the input matrix which is currently covered my the kernel. The image below shows this process in more detail.
In image classification, convolutions are important because they can be used to extract prominent features of the image by filtering out noise.
What is a kernel?
The kernel is simply a smaller matrix which we pass over the” input to the convolutional layer. The kernel has both a shape, and a stride. The shape is in the form of NxMxR where N and M are the width and height of the kernel, and R is how many channels it has. When working with 3 dimensional kernels, its helpful to think of it as a rectangular prism, where N and M are the width and height dimensions, and R is the depth.

The stride of the kernel is simply how many pixels the kernel will move in the horizontal and vertical directions. This can have an impact on the outcome because some pixels may get filtered multiple times, or not at all.
The kernel plays an important role in the outcome of a convolution. The values in the kernel will determine what the outcome of the convolution will be. For example, if you use a Gaussian Distribution in the kernel, the output of the convolution will be a Gaussian Blur. Another interesting kernel is the Sobel Filter, which is for edge detection.
Pooling
Another important aspect of Image classification is Pooling. In our project we used Max Pooling. Max Pooling is used to extract the most expressed features of the image. They do this by passing a kernel over the input and only selecting the maximum value of the input from that pass for output.
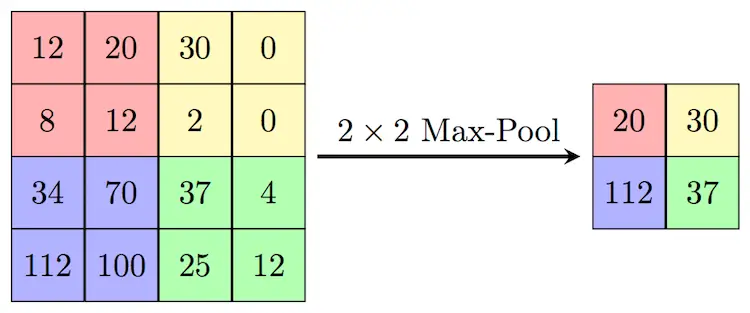
Dropout
Dropout is a regularization method in neural network training in which some layer outputs are ignored or dropped at random. This is done to prevent all the neurons from converging to the same goal. Disallowing neurons to converge onthe same goal seems counterintuitive, however, this has the effect of decorrelating the weights of groups of neurons.
Our Network Architecture
If you search Google for what model architecture to use, you’ll likely come across four different architectures: Resnet50, VGG16, Inceptionv3, and EfficientNet.
We (my partner Joel and I) decided not to go with one of these architectures. Instead we wanted to experiment with the Keras Tuner to see what kind of performance we could come up with on our own.
To come up with this we took an iterative approach. We started with just a basic CNN configuration, just a coupl convolution layers followed by a dense output layer. With this we were able to get around 74% accuracy on the validation dataset. We then iterated by adding a MaxPooling layer after each convolution layer. With this change we were able to get our validation accuracy up to 80%. Then we achieved 83% validation accuracy by simply adding a dropout regularization of 0.5.
Keras Tuner
Now comes the part where we started tuning our architecture with the Keras Tuner. We started with the most basic version of our architecture, the one with just two convolution layers and a dense layer. We decided to tune the model one hyper-parameter at a time. We started with the number of consecutive convolution layers, then we optimized the number of kernel filters. Then added max pooling between each convolution layer and optimized the size and stride of the kernel. Finally, we added a dense layer before the output layer, and optimized the number of nodes for this layer. The final architecture was able to achieve a validation accuracy of 89.8%. See the figure below for details on the model architecture.

Results
Our best model boasts an accuracy of 91.80% on the validation dataset, which is quite strong in a vacuum. However, in testing the final model with data from the internet, we found some weaknesses in it. These weaknesses can largely be attributed to the size of our training dataset, which only has 1027 training images (500 horses, 527 humans). There also exists a bias in our training data. Namely, the dataset is biased towards full body images of humans. Due to this bias, if given an image of a human in which only a portion of the body is visible, say their head, it will misclassify the image. Which leads us to ponder how we can improve the accuracy of our model on more general data.
Discussion
The data shows that the single variable that makes the most impact when changed is the Kernel Size of one or more convolutional layer(s). The experiments focused on the effects of changing a single parameter at a time, however it may be beneficial to allow the tuning of several parameters simultaneously to find the best overall configuration. More excitingly, experimenting with various boosting methods may also lead to improvements.
Additionally, the dataset used was relatively small, and improvements to accuracies could likely be seen when performing data augmentation to boost the number of training data points.
Conclusion
All in all, we would like to do more research into how to optimize a model with a relatively small dataset. But we were particularly happy with the results we got. For more details, our full report.
